About Data Mapping
Data maps are the lynchpins of modern privacy. In this article, we look at how to build the perfect business data map for compliance with laws like GDPR and CCPA.
What is Data Mapping?
In the world of data privacy, data mapping is the process of inventorying the personal data in your business systems. This inventory is called a data map. An up-to-date data map is vital for compliance with modern data privacy regulations – like GDPR in the EU and CCPA in the US.
More than ever, consumers and laws demand that companies account for all the ways they handle consumers’ data.
You might hear a data map called a data flow mapping, a data inventory, an Article 30 assessment (under GDPR), or a personally identifiable information disclosure (under CCPA). However, the concept is the same: a thorough record of the data processing that your company conducts.
Data mapping requires answers to basic questions including:
- What personal data does my company collect?
- When does my company erase this data?
- Why does my company collect and process this data?
- How does my company process this data?
- Besides my company, who else receives this data?
In finance, the company balance sheet provides a high-level accounting of every dollar in a business. Data mapping does the same thing for every cell of PII in every business database. The idea of data mapping is intuitive. However, building one can be daunting. Across industries, data flows are growing larger and becoming more complex. Companies increasingly use third-party tools to process data about consumers’ health, finances, and more. To account for all of these data flows, companies must create a record of the data processing happening in-house and in any third-party apps.
Is this just a nice-to-have? Not if you do business in Europe, California, or an ever-growing list of regions around the world. Data is the fuel for modern enterprise, and will only continue to be more essential. At the same time, more and more data privacy laws are emerging across the globe. In this environment, data mapping is an essential piece of your compliance ops and a demonstration to your users that you respect their data. Below, we dive deeper into the reasons data mapping supports legal compliance and builds user trust.

Why Data Mapping Matters
Compliance
Laws like GDPR require that data-driven businesses build a record of their data-processing activities. They also grant consumers rights to access, correct, or delete their personal information stored by a company. Companies must not only build systems to respect these rights but also maintain an account of how personal data flows through the company.
Data mapping is not going away anytime soon. Since GDPR went into effect in 2018, a growing trend of strong privacy law has swept the globe. California’s CCPA and its upcoming CPRA strongly resemble the GDPR. From Virginia to Brazil, new and upcoming laws are demanding that businesses account for all processing of personal data. Though privacy laws will continue to evolve, one thing is certain: data-driven businesses will need nimble compliance ops. Effective data mapping tools are key to being ready for tomorrow’s regulations.
Trust
Data mapping is not just a formality to check off your compliance to-do list. Because a data map keeps track of where and how your company processes consumers’ data, you are taking steps to earn consumers’ trust. And trust is precious for any business.
75%
of shoppers will prioritize brand trust over price when purchasing a product. (Source: Edelman)
52%
of American consumers decide against using a product or service if they feel the company collects too much personal data. (Source: Pew)
56%
of privacy pros report “locating unstructured personal data” as the most challenging issue in fulfilling subject requests. (Source: IAPP)
Data Mapping Drives Brand Trust
Non-compliance with a law like CCPA not only costs a business a hefty fine – it damages a reputation, which can be even harder to rebound from. Data mapping helps keep your business in line with legal requirements. Further, data mapping simplifies the process for fulfilling users’ requests to access, correct, or delete their information in your systems. When you can quickly retrieve all instances of a user’s data in your databases, you can promptly fulfill their request. In turn, users have a seamless experience in exercising their data rights. They see your business as one that respects their data, one that has earned their trust.
Make the Most of Data Mapping
Manual and Automated Data Mapping Tools
A spreadsheet might have done the job for data mapping ten years ago, but the time has come to move beyond manual methods. Simply put, manual data mapping cannot keep pace with evolving data flows and regulations. To account for not only internal data processing but also third-party applications, teams will need more and more resources to keep up with the sheer volume of data.

Data-driven businesses rely on their team’s ingenuity. When you engage your company’s data experts for months on a manual data map, time spent on data mapping is time lost on innovation. Each new regulation or application in your tech stack could require a re-work of the whole data map. And all of that energy does not guarantee compliance. Human error and inconsistency is all too possible with a manual undertaking.
Instead of sinking time and labor into a manual data map, use automation to build your data map. Automated data mapping introduces efficiencies in the form of trained algorithms and pre-built connectors to audit the structures of large databases. Consistent labeling is key to an effective data map, and automation excels at applying detailed instructions to data. To get the best of both worlds, human review can come together with automated data mapping tools in a hybrid approach. Personnel from your team provide the nuance of human review, ensuring accuracy without risking human error or costly time sinks that come with manual data mapping.
Getting Started with Data Mapping
Your company can appoint an individual – a Data Protection Officer – as the primary staff charged with building and maintaining the data map. To take account of the personal data residing in your company, the Data Protection Officer should inventory all in-house databases as well as third-party applications. As we explain in our primer on building a data map, the inventory is more than a bullet-pointed list of data categories. It’s a systematic review that also includes the retention schedule, purpose of processing, recipients, and other details to meet compliance requirements. This inventory is the foundation of any data mapping effort.
Overcome Common Challenges of Data Mapping
Inconsistent Labels
This challenge is most prevalent with manual data mapping. Huge volumes of data flow through your business from a variety of channels, and an effective data map needs consistency in labeling. Without uniform notation for the types of data collected and processed, a company could overlook a piece of the data flow. This oversight could mean that a Record of Processing Activity is inaccurately completed, jeopardizing your company’s compliance ops.
Solution: An automated data mapping solution keeps labels consistent. Label and data analysis can also keep your company on track to ensure that labels are accurate.
Disparate Data Sources
Companies aren’t just processing more data than they used to. They’re exchanging data with more third-party applications than before, too. Adding a new app to the tech stack – for marketing, messaging, HR, or any purpose – increases the data sources and complexity of the data map. It’s vital that companies know what data flows to what application.
Besides being a regulatory requirement on its own, an accurate record of third-party data flows makes it easier for users to exercise their data rights. When a user requests to access or delete all personal data in your company, comprehensive data mapping makes for an efficient fulfillment of the request. Your team can quickly account for all appropriate data sources. Enacting an access or deletion request across disparate systems and data sources can take serious time and effort. Further, failure to meet these requests within a given window can mean a regulatory fine and damage to your company’s reputation.
Solution: Instead of contacting engineers at each of your company’s third-party applications with a questionnaire about what user data they process, a nimble data map automatically bridges between your systems and third parties.
Bring Top-Tier Data Mapping to Your Company
Automated Data Mapping for Simplified Compliance
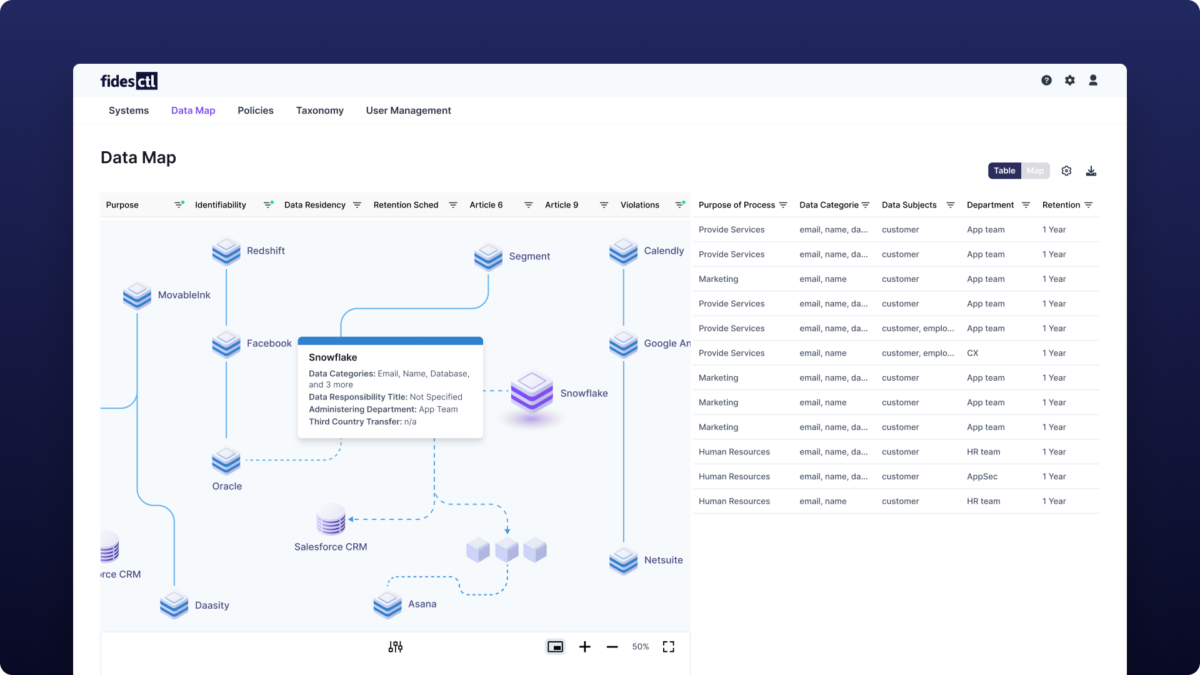
Ethyca makes data mapping straightforward and scalable for your company. Ethyca connects with your databases to account for the personal information in your systems. In addition to in-house data stores, you have your suite of third-party applications. To inventory data in these applications, Ethyca has data integrations. A data integration acts like a bridge to connect with third-party applications. With Ethyca, a data integration typically connects to a third-party app using its API key. It allows Ethyca to access and handle users’ data in these applications, building a complete picture of where your users’ personal data resides. Once you provide the metadata and the basic legal information, data integrations automatically bring users’ data into a single view. Ethyca is constantly growing its large library of data integrations to simplify data mapping across SaaS products.
Because Ethyca and its data integrations are familiar with the data structures of your go-to SaaS applications, the platform can make quick work of problems that might require days of manual effort. One such problem might be standardizing data formats. Perhaps one app stores a users’ first and last name in a single field, while another app stores them in two separate fields. Ethyca automatically takes care of what might otherwise be a thorny problem, without the risks of human error.
Automated Reports
With the help of data integrations to connect with third-party apps’ data, your data map gives a birds-eye view of the personal information flowing through your company. When it comes to fulfilling legal requirements – like the Article 30 inventory under GDPR – Ethyca generates a comprehensive table of the data relationships in your company. This output, available for download directly as a .csv file, delivers the transparency and thoroughness that modern privacy law demands.

The example above fulfills the criteria for GDPR compliance, which is the gold-standard for modern data privacy. The report addresses the following:
- Data Processing Activities: What application processes this data?
- Data Classes: What categories of personal data are being processed?
- Associated Software and Data Stores
- Retention Period: How long is this data stored?
- Transfer to Third Countries: What other countries receive this data
- Categories of Data Subjects: Who provides this data
- Categories of Recipients: Who will receive this data?
Automatic reporting simplifies internal and external compliance reviews. This gives your company peace of mind when it comes to any auditing. Your team can focus on its next innovation and rest assured that users’ personal data is accounted for.
Make Effective Data Mapping a Reality
Data mapping is the bedrock of modern privacy compliance, and it doesn’t need to be overwhelming. We’re here to help you deliver the privacy solutions that regulations require and that your user-base deserves.